How to operate a drone is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to advanced flight maneuvers and image capture techniques. We’ll explore essential controls, navigation methods, and troubleshooting tips, ensuring you gain a comprehensive understanding of responsible and proficient drone piloting.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive resource covers all aspects of safe and effective drone operation. From understanding basic controls and navigating airspace restrictions to mastering advanced techniques and optimizing image quality, we provide a step-by-step approach to help you confidently take to the skies.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s physical components and verifying its operational readiness. Adherence to safety regulations and best practices is equally important to prevent accidents and ensure compliance with local laws.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection should be performed before every flight. This ensures the drone is in optimal condition and minimizes the risk of malfunctions during operation.
| Item | Check | Action Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage, cracks, or looseness. | Replace damaged propellers. Tighten loose propellers. | Ensure all propellers are securely attached. |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition. | Charge battery if necessary. Replace damaged or old batteries. | Use only manufacturer-approved batteries. |
| Camera | Verify camera functionality and lens clarity. | Clean lens if necessary. | Check for proper image stabilization. |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Check gimbal movement and stability. | Calibrate gimbal if necessary. | Ensure smooth and accurate gimbal operation. |
| Sensors | Verify the functionality of all sensors (GPS, IMU, etc.). | Calibrate sensors if necessary. | Ensure accurate position and orientation data. |
| Radio Control System | Check the connection between the remote controller and the drone. | Replace batteries if needed. Reconnect if necessary. | Ensure a strong signal. |
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Responsible drone operation necessitates adherence to relevant safety regulations and best practices. Understanding and following these guidelines is essential for preventing accidents and ensuring the safety of others.
- Always maintain visual line of sight (VLOS) with your drone.
- Avoid flying near airports, heliports, or other restricted airspace.
- Never fly over crowds or people.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Be aware of weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds or rain.
- Always have a backup plan in case of emergencies.
- Familiarize yourself with local drone regulations.
Creating a Safe Flight Plan
A well-planned flight minimizes risks and ensures a smooth operation. This involves considering airspace restrictions, potential hazards, and establishing clear flight parameters.
- Check for airspace restrictions using online resources or apps.
- Identify potential hazards in the flight area (buildings, trees, power lines).
- Establish a clear flight path and altitude.
- Set waypoints if necessary.
- Communicate your flight plan to anyone who might be affected.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls and navigation systems is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section details the functions of common controls and explains different flight modes.
Drone Remote Control Functions
Most drone remotes use two joysticks for controlling the drone’s movement. Each joystick and button performs a specific function.
- Left Joystick (Yaw and Throttle): The left joystick controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and altitude (throttle). Pushing the joystick forward increases altitude, pulling it back decreases altitude. Moving the joystick left or right rotates the drone.
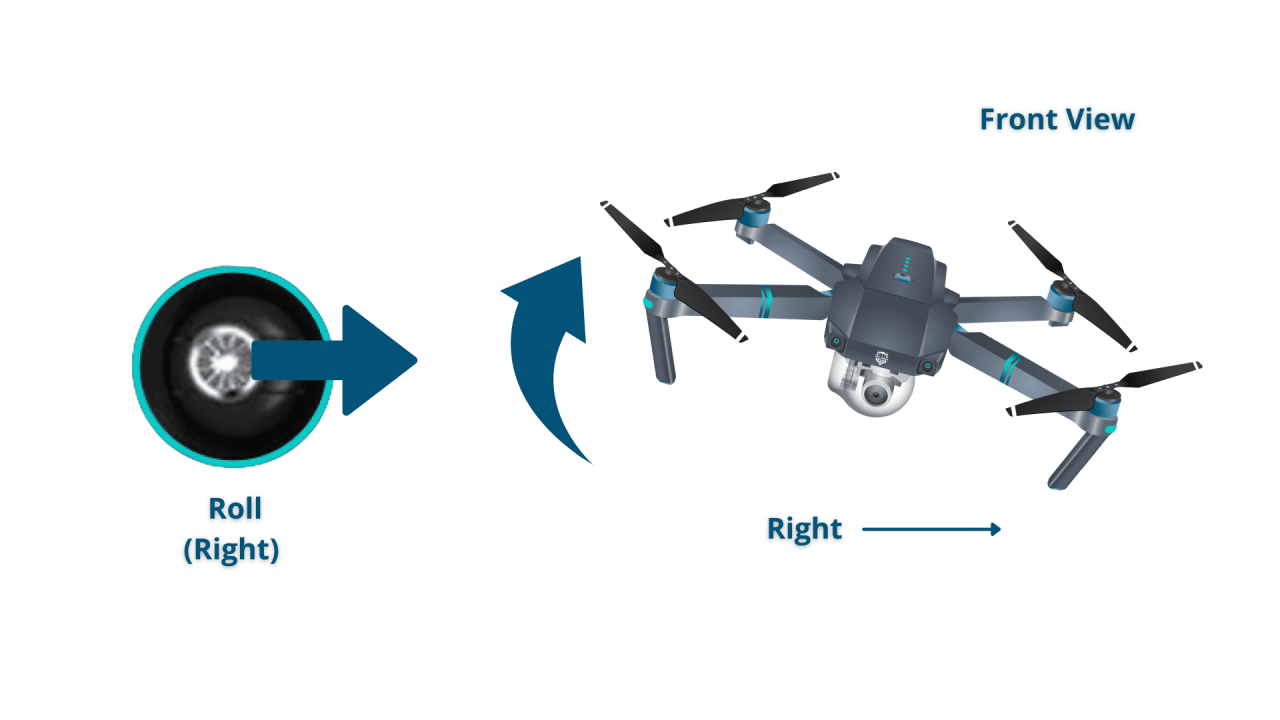
- Right Joystick (Pitch and Roll): The right joystick controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement). Pushing the joystick forward moves the drone forward, pulling it back moves it backward. Pushing it left or right moves the drone sideways.
- Return to Home (RTH) Button: This button initiates the drone’s automated return to its takeoff point.
- Emergency Stop Button: This button immediately cuts power to the motors, causing the drone to descend rapidly.
- Camera Control Buttons: These buttons control the camera’s functions, such as taking photos or recording videos.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Understanding their implications is essential for safe operation.
- GPS Mode: The drone uses GPS signals for position and orientation. This mode provides excellent stability and is ideal for beginners.
- Attitude Mode: The drone relies on its internal sensors (IMU) for orientation. This mode offers more agile control but requires more skill to operate safely.
GPS Navigation and Waypoints
GPS coordinates and waypoints allow for precise drone navigation. This enables creating complex flight paths and automated missions.
Example Flight Path: A simple flight path could involve setting waypoints at specific GPS coordinates to create a square or rectangle pattern. The drone would then autonomously follow these waypoints, capturing images or video along the way. This would require using the drone’s specific flight planning software.
Taking Off, Flying, and Landing: How To Operate A Drone

Safe and controlled takeoff, flight, and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents. This section details the steps involved in each phase of the flight.
Safe Takeoff Procedure, How to operate a drone

Before takeoff, perform all pre-flight checks. Ensure the area is clear and free of obstacles. Start the motors and gently lift the drone off the ground, maintaining a steady ascent.
Maintaining Stable Flight
Maintaining stable flight requires smooth and precise control inputs. In calm conditions, control is relatively straightforward. However, windy conditions require more careful piloting, with adjustments to altitude and speed to maintain stability.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safe operating procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently and safely operate your drone.
Safe Landing Procedure
For a smooth landing, gradually descend the drone to a safe landing spot. Maintain a slow and controlled descent to avoid any sudden impacts. Emergency landing procedures involve using the emergency stop button, but this should be used only as a last resort.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding your drone’s camera settings and techniques for optimal image capture. This section explores camera operation and image optimization techniques.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, responsible drone piloting ensures both safety and successful flights.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
High-quality aerial photography and videography requires understanding and utilizing various camera settings and techniques. Experimentation is key to mastering these techniques.
| Setting | Effect on Image Quality |
|---|---|
| ISO | Higher ISO values increase sensitivity to light, but can introduce noise. Lower ISO values result in cleaner images but require more light. |
| Shutter Speed | Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower shutter speeds can create motion blur. |
| Aperture | Wider apertures (lower f-stop numbers) allow more light to enter the camera, creating a shallower depth of field. Narrower apertures (higher f-stop numbers) result in a greater depth of field. |
| White Balance | Correct white balance ensures accurate color representation. |
Camera Angles and Perspectives
Different camera angles and perspectives can significantly enhance visual storytelling. Experiment with various angles to achieve the desired effect. High-angle shots provide a broad overview, while low-angle shots create a sense of scale and drama.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Image Capture
Optimal camera settings vary depending on lighting conditions. In bright sunlight, lower ISO and faster shutter speeds are often preferred. In low-light conditions, higher ISO values may be necessary, but this may introduce noise. Adjusting the aperture affects depth of field and light intake.
Battery Management and Flight Time Optimization
Effective battery management is crucial for maximizing flight time and preventing unexpected power failures. This section discusses battery care and strategies for extending flight duration.
Drone Battery Management Strategy
Proper battery management involves careful charging, storage, and usage practices. Always use manufacturer-recommended chargers and avoid overcharging or discharging batteries.
| Flight Time | Battery Level | Environmental Factors |
|---|---|---|
| 20 minutes | 70% | Calm conditions, moderate temperature |
| 15 minutes | 50% | Windy conditions, high temperature |
| 25 minutes | 80% | Calm conditions, low temperature |
Note: These values are illustrative and will vary based on drone model and battery condition.
Optimizing Flight Time
Flight time can be optimized by adjusting various flight parameters. Lowering flight speed and altitude reduces energy consumption, extending flight duration. Avoid rapid ascents and descents.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Understanding common drone problems and their solutions is crucial for maintaining operational readiness. This section provides troubleshooting steps for common issues.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
- Loss of Signal: Check for obstructions between the drone and the controller. Ensure the controller’s batteries are fully charged. Try restarting both the drone and the controller.
- Low Battery: Land the drone immediately. Charge the battery according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Malfunctioning Motors: Inspect the motors for damage or debris. Try recalibrating the drone’s sensors. If the problem persists, contact the manufacturer for support.
- GPS Issues: Ensure the drone has a clear view of the sky for optimal GPS signal reception. Try restarting the drone or recalibrating the GPS.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Try recalibrating the gimbal. Check for any physical obstructions.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance and cleaning are crucial for preventing malfunctions and ensuring optimal performance. This includes cleaning the propellers, sensors, and camera lens. Regularly inspect the drone for any signs of damage or wear and tear.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone legally and responsibly requires understanding and adhering to all relevant regulations. This section highlights the importance of legal compliance.
Drone Regulations and Laws
Drone regulations vary by location. It is crucial to research and understand the specific laws and regulations in your area before flying. These regulations often cover airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need to obtain permits or licenses before operating a drone. These permits often cover commercial operations or flights in restricted airspace.
Implications of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can result in fines, legal action, or even criminal charges. It’s essential to prioritize safety and legal compliance when operating a drone.
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section explores advanced flight maneuvers and techniques for enhancing your drone operation skills.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers such as circling, orbiting, and following specific paths require practice and skill. Mastering these techniques enhances the capabilities of your drone and opens up creative possibilities for aerial photography and videography.
Automated Flight and Image Capture
Drone software allows for automated flight and image capture, simplifying complex operations. This software enables the creation of pre-programmed flight paths and automated image acquisition sequences.
Specialized Drone Accessories
| Accessory | Function |
|---|---|
| Gimbal | Provides camera stabilization, reducing image shake and improving video quality. |
| ND Filters | Reduce the amount of light entering the camera, allowing for wider apertures and slower shutter speeds in bright conditions. |
| Propeller Guards | Protect the propellers from damage and enhance safety. |
| Extra Batteries | Extend flight time and provide backup power. |
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of the key elements involved, from pre-flight preparation to post-flight maintenance. By adhering to safety regulations, continuously practicing your skills, and staying updated on the latest technologies, you can confidently and responsibly explore the exciting world of aerial photography and videography.
Remember, responsible drone piloting ensures both your safety and the safety of others.
FAQ Insights
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and autonomous flight modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like obstacle avoidance and return-to-home functionality.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific rules and procedures.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If the RTH fails, attempt to regain signal by moving to a higher vantage point. If still unsuccessful, contact local authorities.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s recommended to calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’re flying in areas with strong magnetic interference.